The U.S. Patent and Trademark Office has granted a patent to a novel technique and device for pasteurizing eggs developed by engineers at the Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory (PPPL) and the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA). The award marks the 27th patent granted to PPPL inventors since 1994.
The invention uses radio frequency (RF) energy to transmit heat through the shell and into the yolk while the egg rotates. Streams of cool water simultaneously flow over the egg to protect the delicate white. Researchers then bathe the egg in hot water to complete the pasteurization process.
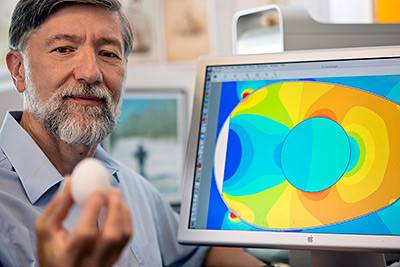
PPPL engineer Christopher Brunkhorst displays an egg while a computer image simulates the levels of radio frequency power that different parts of an egg absorbed during an experiment. (Photo by Elle Starkman, PPPL Office of Communications)
"This is a unique experience for me," said Chris Brunkhorst, an expert in RF heating at PPPL. "It's the first time I've had a patent awarded." Brunkhorst holds the patent with David Geveke, research chemical engineer and lead scientist at the USDA Agricultural Research Service in Wyndmoor, Pennsylvania, and Andrew Bigley, an engineering technician recently retired from the USDA.
The three inventors will share in any revenue that comes from licensing the invention. Princeton University holds joint rights to the technology with the USDA, which is in talks to license it to an industrial user.
The invention can pasteurize shell eggs in one-third the time that current methods require, according to Geveke. And unlike such methods, which heat the eggs in water for about an hour, the invention doesn't affect the appearance of the egg white, he said. The aim is to produce a pasteurized egg "that is hardly discernible from a fresh, nonpasteurized egg," he noted.
Adam Cohen, deputy director for operations at PPPL, applauded the patent as an example of the high quality of the work of laboratory staffers and encouraged researchers, engineers and technicians to disclose their inventions to the PPPL Office of Technology Transfer. "People here are incredibly creative and inventive," Cohen said, "and the process of finding out where their discoveries may lead starts with disclosure."
PPPL, on Princeton University's Forrestal Campus in Plainsboro, New Jersey, is devoted to creating new knowledge about the physics of plasmas — ultra-hot, charged gases — and to developing practical solutions for the creation of fusion energy. Results of PPPL research have ranged from a portable nuclear materials detector for anti-terrorist use to universally employed computer codes for analyzing and predicting the outcome of fusion experiments. The laboratory is supported by the Office of Science of the U.S. Department of Energy and is managed by Princeton University. The Office of Science is the largest supporter of basic research in the physical sciences in the United States, and is working to address some of the most pressing challenges of our time.
