|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
Plastic Deformation |
|||||||||||||||||
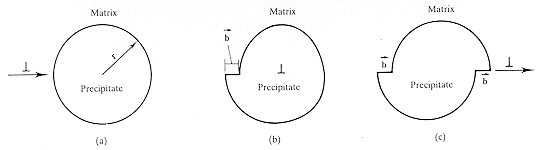
· The shear stress due to dislocation
pile up at a ductile
precipitate particle may cause the particle to
shear and increase its surface area. The area increases as the dislocation enters
and leaves the particle, a distance of 2b. |
|||||||||||||||||
 |
|||||||||||||||||
From:
Courtney, "Mechanical Behavior of Materials," |
|||||||||||||||||
· The particle surface area increases
by 2πrb, where r is the particle
radius. This increase in surface area changes the particle energy by dUS=
2πrbγ, where γ=
surface energy. |
|||||||||||||||||