|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
|
Plastic Deformation |
|||||||||||||||||
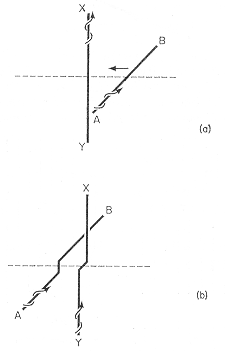
| · The diagram shows
the effect of intersection on two screw
dislocations on orthogonal slip planes. Each dislocation picks up a
jog
equal in magnitude and direction to the Burgers
vector of the dislocation it intersects. · In this case, the two jogs are of edge character and have a length of one interatomic spacing. · The edge-type jog on the moving dislocation has a slip plane (that contains b, t) that is normal to the slip plane in which the screw dislocation is gliding. · The jog can only follow the moving screw by the slow climb process and is essentially fixed in the crystal where it is formed. |
From: Hull, "Introduction to Dislocations," Pergamon (1965) |
||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||