Equation of State
An Equation of
State describes the equilibrium conditions of a system in terms of values
of (p,v,T) that generate the equilibrium surface of state for the substance.
For an Ideal Gas the equation of state has the form: pv = RT,
where R is the Universal Gas Constant ( 8.314 J/ (mol.K))
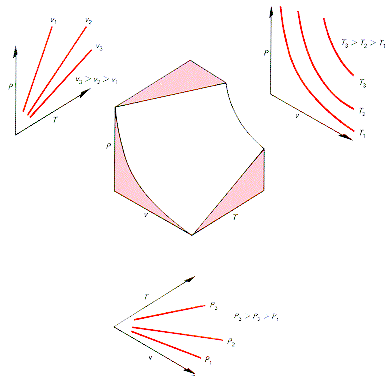
This surface
is shown opposite as well as projections of paths in the surface onto the
(p,T), (p,v) and (T,v) planes.These paths represent equilibrium processes for
constant v, T, and p, respectively.
Diagram from: Howell
& Buckius, "Fundamentals of
Engineering Thermodynamics," McGraw Hill
(1987)