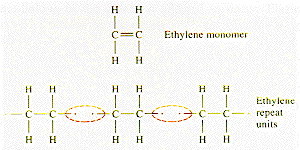
Macromolecules, such as those of polyethylene, are formed by joining together smaller units in the polymerization process. The diagram shows the steps involved in the addition polymerization reaction used to form polyethylene from the ethylene monomer.
In the ethylene monomer the two carbon atoms are connected by a double bond. In the polymerization reaction, this bond is converted to a single bond when the ethylene mer interacts with a free radical and the mer becomes a radical with one free covalent bond. This bond can then interact with another mer, joining them together and creating a radical of larger molecular weight.
From: Askeland,
"The
Science of Engineering Materials," PWS (1994)
This process continues, and the molecular weight of the polymer molecule increases, until the molecule is terminated by a free radical or by joining with another radical chain. The polymerization process is favored by the difference in bond strength between single and double carbon bonds. The single bond has an energy of 88 kcal/g.mole and the double bond 172 kcal/g.mole. Two single bonds are formed for each double bond lost for a net bonding energy gain of 4 kcal/g.mole
| Materials |
| Menu |
| Prev |
| Next |